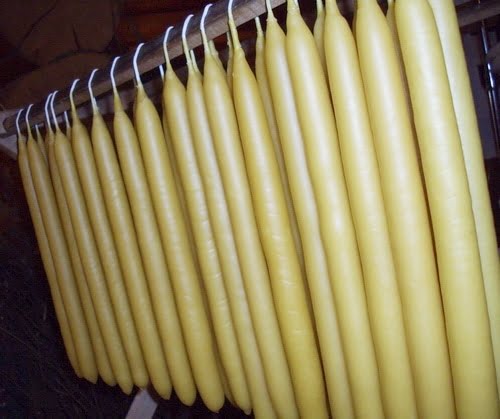
Candle making is a craft that has been practiced for centuries, bringing warmth, coziness, and ambiance to our homes. While there are many factors that contribute to the quality and performance of candles, one important element is hardening wax. In this article, we will explore what hardening wax is and its significance in the candle making process.
At its core, hardening wax is an essential component that helps candles hold their shape and structure. It adds strength and stability to the wax, allowing it to withstand heat, pressure, and variations in temperature without melting or distorting. Hardening wax not only affects the physical properties of the candle but also influences how well it burns.
Understanding the basics of hardening wax is crucial for anyone venturing into candle making. In the next sections of this article, we will delve deeper into what exactly hardening wax is made of and how it works.
We will explore the different types of hardening waxes available in the market, as well as their benefits for enhancing both the quality and performance of candles. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of hardening wax, you will be better equipped to create exquisite candles that stand out from the rest.
Understanding the Basics
Hardening wax plays a crucial role in candle making as it helps to enhance the quality and performance of the final product. It is important for candle makers to understand the basics of hardening wax, including what it is and how it works.
What is Hardening Wax?
Hardening wax, also known as candle hardener, is an additive that is mixed into the wax during the candle making process. It is designed to increase the hardness and durability of the wax once it has solidified. Hardening wax can be made from various materials, including waxes such as beeswax or soy wax, as well as other additives like stearic acid or polyethylene.
How Does Hardening Wax Work?
When hardening wax is added to the melted candle wax, it acts as a strengthening agent, altering the characteristics of the final product. The addition of hardening wax increases the melting point of the candle, making it less likely to warp or become misshapen when exposed to heat. Additionally, hardening wax improves the scent throw and burn time of candles by enhancing fragrance retention and slowing down burn rates.
The mechanism behind how hardening wax works involves its ability to reinforce and stabilize the structure of the candle. As candles cool and solidify, natural waxes can sometimes exhibit shrinkage or cracking due to their inherent properties. This is when hardeners come into play by providing support to prevent structural issues that could arise during cooling.
By understanding how hardening wax functions in candle making, artisans can make informed decisions about which types of hardeners are best suited for their desired finished products.
Types of Hardening Wax
When it comes to candle making, choosing the right type of hardening wax is crucial for achieving the desired results. There are various options available in the market, each with its own set of characteristics and benefits. In this section, we will compare different types of hardening wax commonly used by candle makers.
- Paraffin Wax: Paraffin wax is one of the most popular choices for candle making due to its affordability and versatility. It is a petroleum-based wax that has a high melting point, which makes it ideal for creating long-lasting candles. Paraffin wax can be easily colored and scented, allowing candle makers to create a wide variety of designs and fragrances.
- Soy Wax: Soy wax has gained popularity in recent years due to its eco-friendly nature. It is made from soybean oil and is biodegradable and renewable, making it a sustainable option for candle making. Soy wax burns cleaner and slower than paraffin wax, resulting in longer-lasting candles with less soot and smoke.
- Beeswax: Beeswax is a natural option for hardening wax that has been used for centuries in candle making. It is created by honeybees and has a rich golden color and a sweet scent. Beeswax candles have a longer burn time compared to other waxes, produce little to no soot or smoke when burned, and emit a warm glow that creates a cozy ambiance.
- Palm Wax: Palm wax is derived from palm oil and is known for its unique crystalline appearance when cooled. This type of hardening wax has excellent fragrance retention and produces bright, vibrant colors when dye is added. Palm wax candles have a beautiful textured finish that enhances their aesthetic appeal.
- Gel Wax: Gel wax is a translucent type of hardening wax that creates a unique and beautiful effect when used in candle making. It is highly versatile and can be combined with colorants, fragrances, and accessories to create customized candles. Gel wax candles have a longer burn time compared to other types of waxes and produce a warm, liquid pool of wax as they burn.
When considering the type of hardening wax to use in your candle making process, it is important to consider factors such as cost, sustainability, burn time, fragrance retention, and aesthetic appeal. Experimenting with different types of waxes will allow you to discover the one that best suits your preferences and creates candles of high quality and performance.
Benefits of Hardening Wax for Candle Making
When it comes to candle making, the use of hardening wax plays a crucial role in enhancing the overall quality and performance of the candle. This section will explore the various benefits that hardening wax brings to candle making, highlighting how it improves factors such as burn time, fragrance retention, and color stability.
One of the primary benefits of using hardening wax is its ability to improve burn time. Hardened wax has a higher melting point compared to softer waxes, allowing candles to burn slowly and more evenly. This results in longer-lasting candles that provide hours of enjoyment for candle enthusiasts. By choosing the right type of hardening wax specifically formulated for longer burn time, candle makers can ensure that their creations offer exceptional value to their customers.
Additionally, hardening wax provides improved fragrance retention in candles. Fragrance oils are often added during the candle making process to give a pleasant aroma when lit. However, without proper hardening wax, these fragrances can dissipate quickly during burning. By using a high-quality hardening wax, candle makers can enhance the fragrance throw and ensure that it lasts throughout the entire lifespan of the candle.
Another advantage of incorporating hardening wax in candle making is its ability to maintain color stability. Colors added to candles can fade or change during burning if not properly stabilized. However, with the use of hardening wax, colors remain vibrant and true even after extended periods of burning. This allows candle makers to create visually appealing candles that retain their aesthetic appeal over time.
Step-by-Step Guide
Using hardening wax in the candle making process is essential for creating high-quality candles that have a longer burn time and maintain their shape even in warmer temperatures. In this step-by-step guide, we will walk you through how to use hardening wax effectively to enhance the overall performance of your candles.
- Choose the right type of hardening wax: Before starting, it’s important to understand the different types of hardening wax available and choose one that suits your specific candle making needs. Some popular options include paraffin wax, soy wax, and beeswax. Each type has its own unique characteristics and melting points, so be sure to research and select the best option for your candles.
- Prepare your work area: Clear a clean and spacious workspace where you can safely melt the hardening wax without any obstructions. Make sure to lay down protective coverings or use a double boiler to ensure a safe melting process. It’s crucial to follow proper safety procedures when working with hot wax to avoid accidents or injuries.
- Heat and melt the hardening wax: Begin by placing the desired amount of hardening wax pieces into your chosen melting container or double boiler setup. Gently heat the wax over low heat until it reaches its recommended melting point. Stir occasionally with a heat-resistant utensil until it is completely melted and smooth.
- Add fragrance or color (optional): Once the hardening wax has melted completely, you can add fragrance oils or color dyes if desired. Be sure to follow the recommended guidelines for each fragrance or dye you are using to achieve the desired scent or color intensity. Mix well until all additives are fully blended into the melted wax.
- Pour into candle containers: Carefully pour the melted hardening wax into your chosen candle containers, such as glass jars or molds. Take caution not to spill any hot wax and ensure that each container is filled evenly to prevent any air pockets or uneven burning. Allow the wax to cool and solidify completely before moving onto the next steps.
By following this step-by-step guide, you can effectively incorporate hardening wax into your candle making process for improved candle quality and longevity. Remember to always prioritize safety when working with hot wax and experiment with different types of hardening wax to find the best fit for your candle making projects.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When working with hardening wax for candle making, it is important to be aware of certain common mistakes that can occur and learn some helpful tips and tricks to avoid them. By being mindful of these potential pitfalls, candle makers can ensure a successful and seamless candle making process.
Inadequate Temperature Control
One common mistake when working with hardening wax is not properly controlling the temperature. It is crucial to maintain the appropriate temperature range throughout the entire candle making process. If the temperature is too high, the wax can become overheated, leading to discoloration or even burning.
On the other hand, if the temperature is too low, the wax may not melt completely or may solidify too quickly before pouring into molds. To avoid this mistake, always use a reliable thermometer to monitor and regulate the temperature of the wax.
Incorrect Wax-to-Fragrance Ratio
Another mistake that can affect the quality of candles is using an incorrect wax-to-fragrance ratio. Adding too much fragrance oil can lead to issues such as poor scent throw, excessive smoke when burned, or even a weakened wick.
Conversely, using too little fragrance oil may result in a weak scent or lack of fragrance altogether in the finished candles. It is essential to follow specific guidelines from fragrance manufacturers or conduct test batches to determine the ideal ratio for each type of fragrance oil used.
Neglecting Proper Cooling Time
Allowing sufficient cooling time for candles after pouring is crucial for their overall quality and performance. Rushing this step can result in several issues such as uneven surfaces, frosting (a white crystalline appearance on the surface), or concave tops due to shrinkage as the candle cools down.
It is advised to let candles cool at room temperature for at least 24 hours before handling or moving them. This allows proper solidification and minimizes the risk of creating imperfections in the finished candles.
By keeping these common mistakes in mind, candle makers can avoid potential issues and create high-quality candles using hardening wax. Additionally, incorporating good practices such as maintaining proper temperature control, using accurate wax-to-fragrance ratios, and allowing sufficient cooling time will contribute to the success and satisfaction of their candle making endeavors.
Troubleshooting
Even with proper knowledge and experience, candle makers may encounter challenges when using hardening wax in their candle making process. Understanding how to troubleshoot these issues can help ensure a successful outcome. Here are some common challenges and solutions to consider:
- Uneven Cooling: One common issue candle makers face is uneven cooling of the wax, which can result in an uneven surface or cracking. To address this, it’s important to pour the wax at the correct temperature and avoid rapid cooling. Slowly cool the candles in a draft-free environment at room temperature to prevent cracking.
- Frosting: Frosting refers to the white haze that sometimes appears on the surface of candles cooled with hardening wax. This is a natural occurrence called crystallization and doesn’t impact the performance of the candle. However, if you prefer a smooth appearance, there are ways to minimize frosting. Try pouring the wax at a slightly higher temperature or using additives like stearin or vybar to reduce frosting.
- Poor Adherence: Some candle makers may find that their wicks do not adhere well to hardening wax or peel away from the candle as it burns. This can be frustrating but can be resolved by using a suitable adhesive specifically designed for candle making. It’s crucial to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer and properly secure the wick during pouring.
- Sinking or Pooling: Sinking or pooling occurs when there is excessive shrinkage while cooling, resulting in an uneven surface or hollows within the candle itself. To prevent sinking or pooling, ensure that you are pouring your candles at the appropriate temperature and allowing them enough time to cool completely before handling them.
- Fragrance Issues: Sometimes, adding fragrance oils to your hardening wax can cause problems such as poor scent throw or discoloration. To avoid this, use fragrance oils specifically formulated for candle making and follow the recommended usage rates. It’s also important to test your fragrance oils before using them in larger batches of candles.
By being aware of these common issues and proactively troubleshooting them, candle makers can overcome challenges and create high-quality candles using hardening wax. Experimenting with different techniques, additives, and adjusting various factors like temperature and cooling times can help achieve desired results in candle making.
Advanced Techniques
Once you become comfortable with the basics of using hardening wax in candle making, you may find yourself wanting to explore more innovative ways to incorporate it into your candle designs. Fortunately, there are several advanced techniques that can take your candle making skills to the next level and help you create unique and stunning candles.
One technique that can add a touch of elegance to your candles is called “dipping.” This involves repeatedly dipping the wick into melted hardening wax to build up layers and create interesting textures on the surface of the candle. By carefully controlling the temperature of the wax and the speed at which you dip, you can achieve different effects such as smooth, glossy finishes or rough, textured surfaces.
Another advanced technique is called “marbling.” This involves adding different colors or even metallic accents to your hardening wax before pouring it into a mold. By swirling these colors together in a controlled manner, you can create beautiful marbled patterns within the candle. The key to successful marbling is to work quickly and deliberately before the wax starts to harden.
If you’re feeling particularly adventurous, you might want to try your hand at “embedding” objects within your candles. This involves placing small decorative items such as dried flowers, gemstones, or even seashells into the melted hardening wax before pouring it into a mold. As the wax hardens around these objects, they become suspended within the candle, creating an eye-catching focal point.
Incorporating these advanced techniques into your candle making not only allows for more creative expression but also gives your candles a distinctive and artistic touch. As with any new technique, it’s important to practice and experiment before perfecting these methods. With patience and persistence, you’ll be able to master these innovative ways of using hardening wax in your candle designs.
Alternative Options
There is an increasing demand for natural and eco-friendly products in various industries, including candle making. In response to this demand, alternative options for hardening wax have emerged that are not only effective but also sustainable. These natural and eco-friendly hardening waxes offer candle makers the opportunity to create high-quality candles while minimizing their environmental impact.
One popular alternative option for hardening wax is soy wax. Soy wax is made from hydrogenated soybean oil, which is a renewable resource. It offers several benefits for candle making, such as a longer burn time and cleaner combustion compared to traditional paraffin waxes. Soy wax also has excellent fragrance-holding capabilities, allowing the candles to release a stronger scent. Additionally, it is biodegradable and produces fewer toxins when burned, making it a more environmentally friendly choice.
Another natural and eco-friendly option for hardening wax is beeswax. Beeswax is produced by bees and has been used for centuries in candle making. It has a natural golden color and a sweet scent that adds charm to candles. Beeswax has a higher melting point than other waxes, which results in longer burning times. It also emits negative ions when burned, improving air quality by neutralizing pollutants like dust and pollen.
Coconut wax is another alternative option that has gained popularity among eco-conscious candle makers. Coconut wax is derived from the meat of coconuts and provides a smooth and creamy texture to candles. It has excellent fragrance retention and burns cleanly without producing black soot or toxins. Coconut wax is also biodegradable and sustainable since coconuts are a renewable crop.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, hardening wax is an essential component in the candle making process that plays a crucial role in enhancing the quality and performance of candles. By understanding the basics of what hardening wax is and how it works, candle makers can make informed decisions about which type of wax to use. Comparing different options allows for greater flexibility in creating candles with desired attributes such as hardness, texture, and burn time.
The benefits of using hardening wax in candle making are significant. It not only improves the overall quality of the candle but also enhances its performance by providing a longer burning time and better fragrance throw. Additionally, hardening wax ensures that candles retain their shape, resist melting in warmer temperatures, and maintain a smooth appearance throughout their lifespan.
To effectively incorporate hardening wax into the candle making process, a step-by-step guide provides clear instructions on how to properly use it. This includes suggestions on when and how much hardening wax to add to achieve desired results. It is important to avoid common mistakes such as overheating or overmixing the wax while working with it.
Innovative techniques allow candle makers to explore new ways to utilize hardening wax in their designs. This could involve experimenting with different patterns, textures, or layering techniques to create visually stunning candles. Additionally, alternative options such as natural and eco-friendly hardening waxes provide environmentally-conscious alternatives for those seeking more sustainable choices in their candle making practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you harden wax for candles?
When it comes to hardening wax for candles, there are a few different techniques that can be employed. One common method is the double-boiler method, where you place the wax in a heatproof container and then set that container into a larger pot filled with water. The water should be heated gently so that the wax melts slowly and evenly.
Another way to harden wax is by adding certain additives or hardening agents such as stearic acid, which can increase the melting point of the wax and make it harder when cooled. This can be done by simply mixing the additive into the melted wax before pouring it into candle molds.
What is the best hard wax for candles?
The best hard wax for candles depends on several factors, including personal preference and intended use. Some popular choices among candle makers include soy wax, beeswax, and paraffin wax. Soy wax is often favored for its natural origins and eco-friendly properties, as well as its ability to hold fragrance well.
Beeswax is known for its natural sweet scent and beautiful appearance when used in candles, while paraffin wax is highly versatile and offers excellent scent throw. Ultimately, the best hard wax for candles will depend on what qualities you prioritize in your candle-making process.
What can be used to harden a wax?
Various materials can be used to harden a wax depending on the desired outcome. One commonly used substance is stearic acid, which can help raise the melting point of the wax and make it harder upon solidification. Other options include additives like microcrystalline waxes or polymers that can enhance hardness while also improving burn quality or scent retention in candles.
Additionally, incorporating small amounts of additives such as calcium carbonate or baking soda may contribute to creating a firmer texture in some cases. It’s important to note that while these methods can help increase hardness, finding the right balance between hardness and other desirable characteristics like fragrance throw or burn time is crucial for optimal candle quality.

Welcome to my candle making blog! In this blog, I will be sharing my tips and tricks for making candles. I will also be sharing some of my favorite recipes.